In the world of procurement, efficiency is everything—especially when it comes to managing low-value, frequently ordered items like cleaning supplies, office stationery, or recurring maintenance services. That’s where Blanket Purchase Orders (BPO) come in. A blanket PO is a long-term agreement between a buyer and supplier that allows for multiple purchases under a single purchase order over a defined period.
Businesses often use blanket purchase orders for consumable materials to save time, reduce administrative costs, and streamline their SAP procurement processes. In this blog, we’ll explore how blanket POs work, when to use them, and the step-by-step process to create them in SAP using transactions like ME51N, ME21N, and MIRO.
Why Use Blanket Purchase Orders?
A Blanket Purchase Order is particularly useful when dealing with repetitive purchases of low-cost items from the same vendor. Instead of creating a new PO for every order, you can issue a single PO valid for months or even a year, up to a specified value limit.
Key Benefits:
- Reduces processing time and cost
- Eliminates the need for material master records
- No goods receipt posting required
- Ideal for consumables and indirect materials
- Simplifies invoice processing
Business Scenario Example
Let’s say your company requires janitorial supplies every two weeks. Creating a new PO every time you need cleaning products would be inefficient. Instead, by setting up a blanket PO with a vendor, you can call off deliveries as needed while staying within the agreed spending limit.
This type of procurement not only reduces paperwork but also lowers the total transaction cost, especially when the value of the items doesn’t justify issuing multiple standard POs.
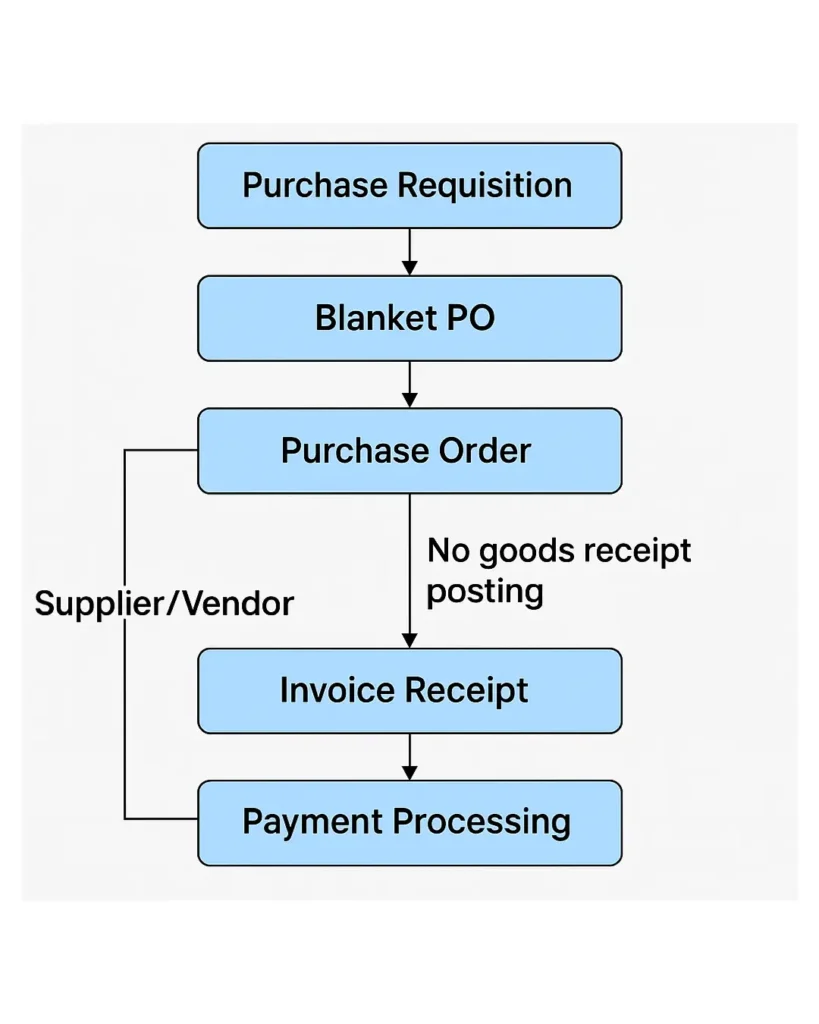
Blanket PO Process Flow
Here’s a high-level view of how the Blanket Purchase Order process works:
- Purchase Requisition (ME51N)
- Blanket PO Creation (ME21N)
- Invoice Posting (MIRO)
- No Goods Receipt Required
Since these orders are for services or consumables, there’s no need to post a goods receipt. Once the invoice is received, it’s matched and paid without requiring physical confirmation of goods.
Step-by-Step: How to Create a Blanket Purchase Order in SAP
Step 1: Create a Purchase Requisition (T-code: ME51N)
- Document type: FO (Framework Order)
- Item category: B (Limit)
- Specify quantity, unit of measure, plant, and overall value limit
- Use appropriate account assignment category (e.g., cost center)
Step 2: Create the Blanket PO (T-code: ME21N)
- Refer to the requisition created earlier
- PO type: FO
- Item category: B (Limit)
- No material number is required
- Enter validity start and end date
- You can use account assignment category U (unknown) if specific cost centers aren’t defined
This PO will allow multiple invoices to be posted until the validity period expires or the value limit is reached.
Step 3: Post the Invoice (T-code: MIRO)
- Enter PO number, invoice date, and amount
- The system auto-copies line items from the PO
- You can simulate the account posting before final posting
- Save and forward to accounting for processing
Cost-Saving Impact of Blanket POs
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt blanket POs is cost efficiency. In many organizations, the cost of creating and processing a standard PO far exceeds the actual value of the consumables being purchased. With blanket POs, you reduce administrative overhead, speed up procurement, and gain better control over vendor spending.
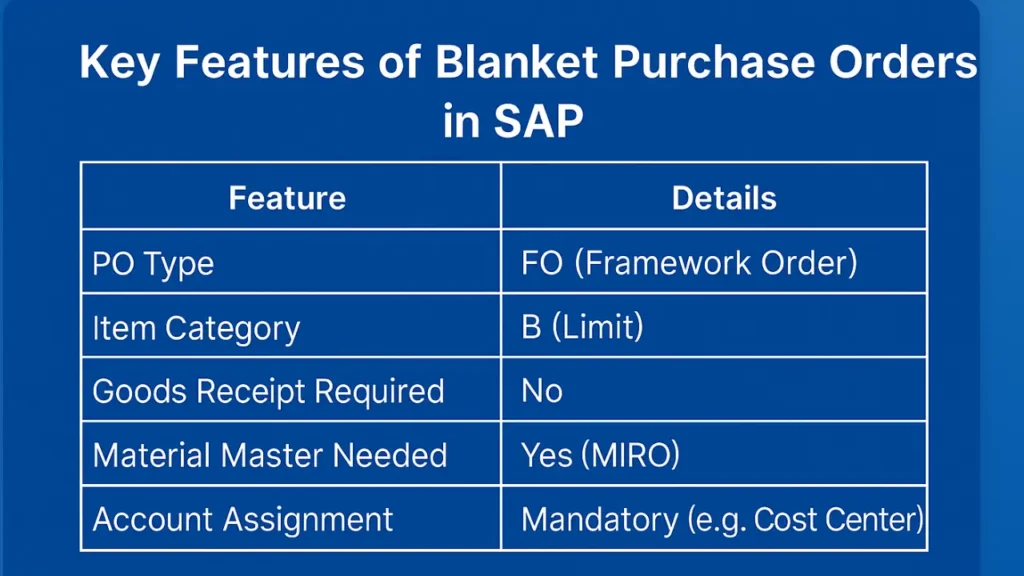
Key Features of Blanket Purchase Orders in SAP
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| PO Type | FO (Framework Order) |
| Item Category | B (Limit) |
| Goods Receipt Required | No |
| Material Master Needed | No |
| Invoice Reference | Yes (MIRO) |
| Account Assignment | Mandatory (e.g., Cost Center) |
Conclusion
Blanket Purchase Orders in SAP are a smart solution for organizations that frequently procure consumable or low-value items. They help simplify the purchasing process, reduce unnecessary work, and lower operational costs. By following the simple steps using ME51N, ME21N, and MIRO, procurement teams can enhance productivity and maintain control over supplier relationships.







