NASA and ISRO are working together on the NISAR satellite, which will use sophisticated radar technology to watch our planet in a way that has never been done before. This satellite is like Earth’s personal health scanner, keeping track of everything from earthquakes to crop growth in a world where climate patterns change quickly and natural calamities happen all the time.

How does this partnership between the US and India operate, and why is it important for people like you and me? Let’s take it apart.
What is NISAR and why it matters
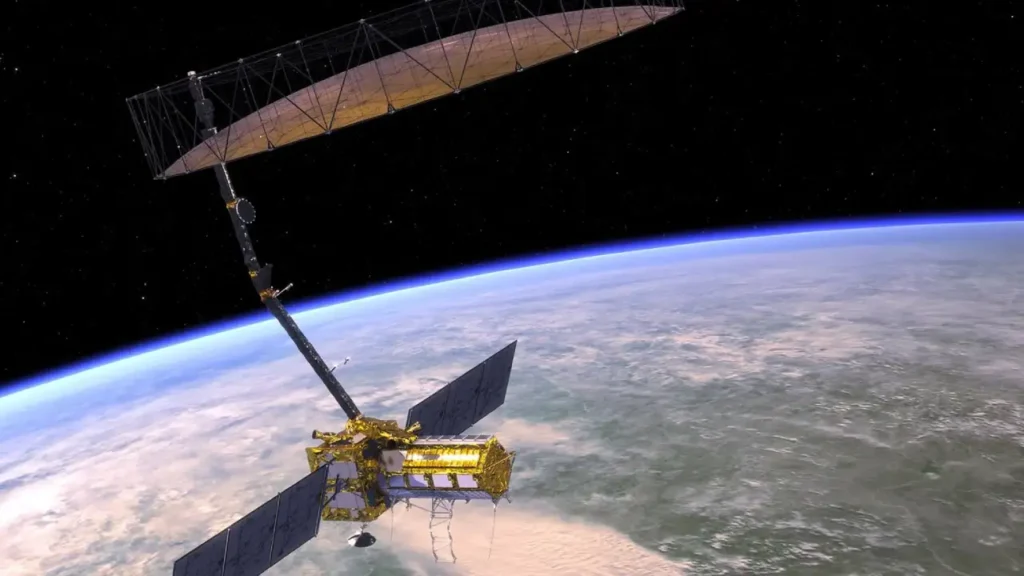
NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization worked together to build the first large-scale satellite mission, ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar. It will use two powerful radar systems, one from NASA and one from ISRO, to map the whole Earth every 12 days.
The goal of the mission is to learn more about how the surface and environment of Earth change. It can keep an eye on things like how the ground moves before earthquakes, how glaciers develop, and even how crops are doing on farms.

NISAR will assist scientists and governments make smarter choices, especially when it comes to managing disasters, water resources, agriculture, and infrastructure planning.
How NISAR works simplified
Imagine taking a picture of the Earth with radar waves instead of visible light. Radar waves can go through clouds, rain, and even some layers of plants.
Here’s how it does that:
- It carries two types of Synthetic Aperture Radar systems.
- L band radar from NASA with longer wavelength
- S band radar from ISRO with shorter wavelength
- Both radars bounce microwave signals off the Earth’s surface and then capture the reflected signals.
- These signals are converted into high resolution data that shows changes in Earth’s surface over time.
NISAR is remarkable since it has a dual frequency radar system. It can find both big changes and small ones, like changes in soil moisture or ice movement.
Real world benefits of NISAR satellite
NISAR is not just another space mission It has practical value on the ground for millions of people.
1.Natural Disaster Monitoring
Helps detect early signs of earthquakes landslides and volcanic activity by measuring ground deformation.
2.Flood and Storm Preparedness
Can track water movement in flood-prone areas or coastal regions vulnerable to hurricanes and cyclones.
3.Crop Health and Food Security
Monitors soil moisture and crop patterns helping farmers and agricultural planners improve yields and reduce loss.
4.Climate Change and Ice Monitoring
Tracks melting glaciers and ice sheets especially in Antarctica to study sea level rise.
5.Infrastructure and Urban Planning
Detects surface shifts that can weaken roads dams or buildings before visible damage occurs.
What makes the technology unique
The radar antenna on NISAR is almost 12 meters wide and opens up in space like a giant sunflower. This lets it scan big areas all at once using a process called Sweep SAR.
Some standout features:
- Maps entire globe every 12 days
- Collects up to 80 terabytes of data products per day
- Works day and night all weather no cloud interference
- Uses full polarimetric and interferometric modes for detailed observation
- Data will be cloud distributed for open access globally
India and USA working hand in hand
This endeavor is a great example of people from all across the world working together. NASA has given ISRO the L band radar high-speed data systems and communication hardware. ISRO has manufactured the spacecraft bus S band radar and will launch the satellite from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
Through cooperative testing and design, both teams have put their parts together. NISAR shows how science may bring countries together for a common goal.
How NISAR compares with other Earth satellites
| Feature | NISAR Satellite | Standard Earth Satellites |
|---|---|---|
| Radar Bands | Dual L and S band | Usually single band |
| Resolution | High and detailed | Medium |
| Cloud and Night Operation | Yes | Limited |
| Data Sharing | Open and cloud based | Often restricted |
| Collaboration | NASA and ISRO | Single country |
Conclusion
NISAR satellite is not just a powerful piece of technology in space but a mission with real impact for people on Earth. Its ability to track changes in the planet’s surface in near real time will be critical for disaster response agriculture environmental conservation and urban development.
As climate events grow more unpredictable tools like NISAR are no longer optional they are essential.
Would you trust a space satellite to help predict floods or save crops Let us know how you think NISAR could be useful in your region.