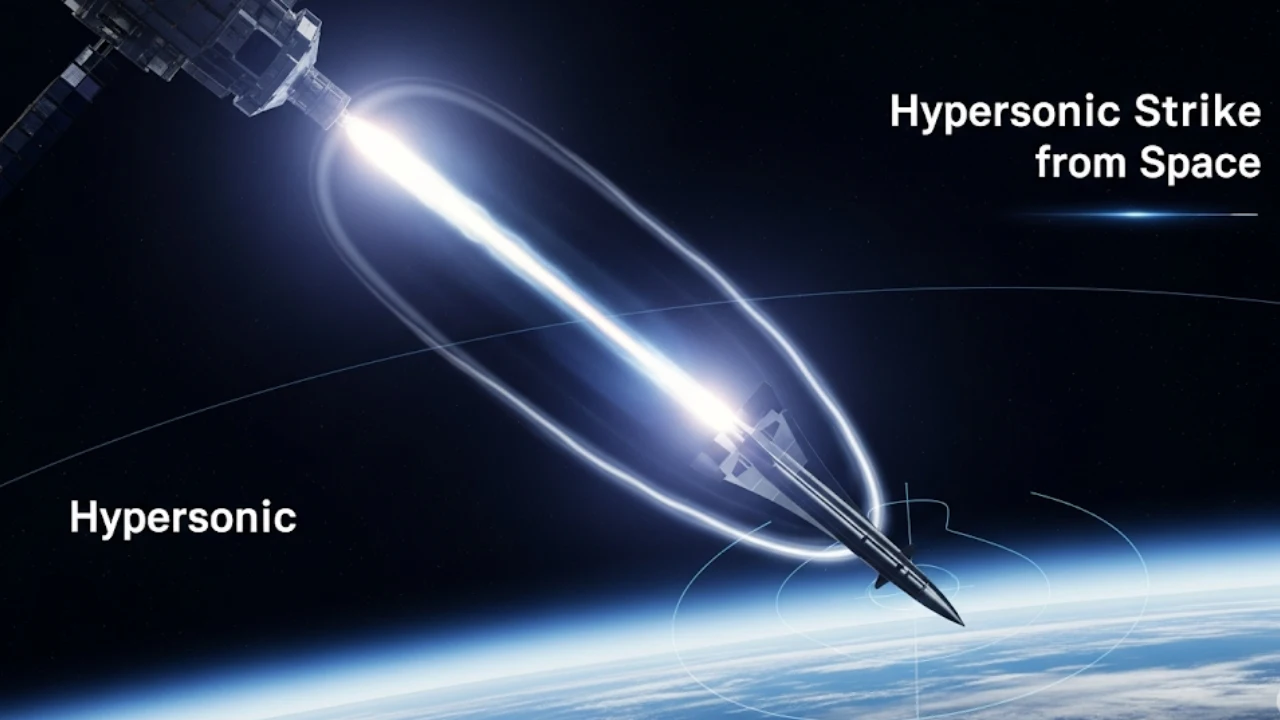
In a startling leap forward, China has reportedly developed space-launched hypersonic missiles capable of striking any target on Earth within 30 minutes. This breakthrough, confirmed by the PLA Rocket Force’s 2025 documentation, poses a significant threat to global strategic stability—especially for countries like India and the United States. With the integration of hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) technology and a space-based launch system, China has ushered in a new era of warfare where missile defense systems may no longer be enough.
What Is a Space-Launched Hypersonic Missile?
The Core Concept
Unlike traditional ballistic missiles, China’s new missiles use a two-stage system:
- Orbital Launch: A missile is launched from space—either from satellites or a space station.
- Re-entry & Glide Phase: After re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere, a hypersonic glide vehicle detaches and flies at Mach 20 (~21,000 km/h), maneuvering unpredictably toward its target.
This system is known as the Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS). The missile never completes a full orbit, making its trajectory harder to detect and giving it global reach—a true “strike-anywhere” weapon.
How Hypersonic Glide Vehicles Work
HGVs represent the most advanced type of missile technology. Here’s how they function:
- Speed: Mach 20 (20x speed of sound)
- Altitude: Mid-range between traditional ballistic and cruise missiles
- Flight Pattern: Unpredictable, unlike ballistic arcs
- G-Force Handling: Can withstand 3–5 g-force maneuvers
These characteristics make interception nearly impossible for current missile defense systems, such as the U.S. THAAD or India’s Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD).
Timeline of China’s Hypersonic Program
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2010 | R&D began on hypersonic technology |
| 2017 | Successful test of the DF-ZF hypersonic glide vehicle |
| 2021 | Global strike testing expanded |
| 2025 | Confirmed space-launch capability via PLA publication |
China’s advancements have been methodical and well-funded, with a clear focus on becoming a dominant player in space warfare and missile technology.
Global Strategic Implications
The implications of China’s space-launched hypersonic missile are profound:
1. U.S. and NATO on Alert
- Threatens U.S. naval carrier groups in the Indo-Pacific
- Challenges continental U.S. missile defense coverage
2. India’s National Security
- India must now factor space-based threats into its defense posture
- Could spur investment in anti-satellite (ASAT) and early-warning radars
3. Weaponizing Space
- China’s use of satellites and space stations for missile deployment blurs the line between peaceful space use and militarization
- May violate the spirit of the Outer Space Treaty, prompting a new space arms race
Countermeasures in Development
Nations are responding with urgency. Here are some emerging technologies:
China’s Side:
- Microwave Photonic Radars: These advanced radars can track multiple hypersonic targets, increasing accuracy and reaction time.
U.S. and Allies:
- Raytheon’s AN/TPY-2 Radar: Designed to track faster, low-orbit projectiles.
- Patriot PAC-3 MSE: Now being installed on U.S. Navy ships to target maneuvering threats.
- Space-Based Interceptors: Under development to counter threats before re-entry.
Why This Technology Is Nearly Unstoppable
Traditional missile defense relies on early detection, trajectory prediction, and high-speed interception. Hypersonic glide vehicles break all three rules:
- They don’t follow ballistic paths.
- They fly too fast for most radars.
- They can change direction mid-flight.
As a result, experts believe that current defense systems are not enough to counter this new class of weapons.
What Experts Are Saying
“This is not just an evolution in missile tech—it’s a revolution. We’re entering an era where space itself becomes the launchpad for conflict.”
— Dr. Michael Griffin, Former U.S. Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering
What’s Next? Global Policy and Preparedness
Governments and international organizations must now:
- Redefine space treaties to address weaponization risks
- Invest in space-based sensors and interceptors
- Accelerate AI-based threat detection for real-time response
India, in particular, must enhance coordination between ISRO, DRDO, and its armed forces to stay ahead of this growing challenge.
Key Takeaways
- China’s space-launched hypersonic missiles represent a new class of global threat.
- The use of hypersonic glide vehicles and the FOBS system make these weapons nearly impossible to intercept.
- U.S., India, and global powers are now racing to build countermeasures.
- This development marks the beginning of space as a battlefield, where geopolitics, technology, and defense intersect.
Final Thoughts
China’s space-based hypersonic missile capability isn’t just about raw power—it’s about strategic dominance in a future where orbit is the new frontline. As global tensions rise, it’s clear that nations must invest in next-gen defense technologies and rethink the rules of warfare—both on Earth and above it.